Economics_RS Class 22
A BRIEF OVERVIEW OF THE PREVIOUS CLASS (05:03 PM)
INFRASTRUCTURE (05:08 PM)
- Discussion on issues related to Infrastructure financing and solution taken by Government
-
Bonds Shares Mutual Funds Risk Low risk Risk is high Risk is moderate in comparison to Shares Return Fixed return Returns are high Return is less in comparison to shares Financial knowledge Requires financial knowledge Less financial knowledge is required. Type of return Interest Dividend Fund manager No fund manager No fund manager Fund manager- Portfolio creation - IDFCs- These can be established as Mutual Fund companies or NBFCs. If IDFC can be set up as MF then it will be regulated by SEBI and if it is set up as NBFC then it will be regulated by RBI. In Mutual Funds, it can not be sold in the secondary market
-
Banks NBFCs Both types of deposits can be opened-Demand deposit+ Term deposit NBFC-D take deposits, Whereas Non-deposit taking NBFCs do not take deposits.
Also, NBFC-D only takes Term depositsBanks to maintain CRR, SLR They do not maintain SLR, CRR
INFRASTRUCTURE FINANCING (05:42 PM)
- It is a challenge in India. According to the 11th Five-year plan, approximately 45% of total infrastructure funding is coming from the government's budget and 55% is managed through debt and equity sources. Banks play an instrumental role in infrastructure financing.
- Challenges in infrastructure financing
- The fiscal burden of the government.
- Asset liability mismatch for the banks
- The bond market is still not developed in India. [Corporate Bond market, Municipal bond market]
- Investment obligation on Insurance and Pension fund companies.
- Increase in funding gaps, especially after the 2008 sub-prime crisis (ECBs route got affected after 2008)
- Legal and procedural issues including land acquisition and administration- land acquisition issues, stalled projects.
- Regulatory cholesterol- The government is excessively controlling the sector.
- Insurance and pension fund companies are better enough to invest in infrastructure as they have a long gestation period, but IRDA guidelines restrict them to invest in Infrastructure sectors.
- Measures taken by the government
- PPP projects in infrastructure- Government faces tight budgetary constraints in the rule-based fiscal policy framework. It was important to encourage the private sector to invest in infrastructure.
- Viability gap funding- It was introduced in 2006, where the central government provides 20% of the total capital cost with respect to PPP projects. (20% by the government, and 20% by the sponsoring authority).
- Setting up of infrastructure debt fund companies- RBI and SEBI notified guidelines for setting up of IDFCs in the form of NBFCs and Mutual Fund Companies.
- The government has reduced the withholding tax on interest payments from 20% to 5%. Infrastructure debt fund companies are expected to channel funds from insurance companies, pension funds, and other long-term sources.
- Rationalization of ECBs- Allowing more ECBs into India with limited restrictions.
- Introduction of credit default swaps which will strengthen the banking sector.
- Take out financing mechanism- It is a mechanism through which short-term funds are used for funding mid-term or long-term projects.
- National infrastructure pipeline- With an investment of 111 lakh crore for 9000 projects, the government started focusing on infrastructure with a primary objective of reaching a $5 trillion economy by 2025.
- NIP is hosted in Invest India Grid portal which is a centralized portal under the DPIIT (Department for Promotion of Industry and internal trade, Ministry of Commerce).
- NATIONAL MONETISATION PIPELINE (06:32 PM)
- It is based on the principle of asset creation through monetization.
- Government leases out its public assets and through the revenue generated from the existing brownfield projects, the government is going to build new Greenfield projects.
- National logistics policy- It mainly aims to bring down the logistics cost to 8% of the GDP by 2030. The government's logistic policy mainly focuses on the multi-modal logistic path (50 crores minimum statement), cold-chain facilities, 15 crores minimum investment, warehouses (25 crores minimum investment)
- PM GATI SHAKTI- It is related to governance. Ministries and departments will talk with each other and public money will not be wasted
PUBLIC-PRIVATE PARTNERSHIP (07:02 PM)
- PPP
- The government typically has several objectives to perform like infrastructure development, welfare mechanism, getting good value for money, timely delivery of services, and meeting public needs. PPPs have shown their potential as an important tool to meet these objectives and address infrastructure shortages.
- These projects provide new sources of capital for public infrastructure development by shifting the responsibility for arranging the finances to the private sector
- PPP refers to a contractual agreement between a government agency and a private sector entity that allows for greater participation in public infrastructure projects.
- Challenges for PPP projects
- "Lack of easy exit"
- "Chakravyuh challenge"- Indian economy is characterized by “Marketism” without exit. This is called the Chakravyuha Challenge of the Indian economy.
- "Regulatory Cholesterol"- Government regulations+ Cutting down ministries, compliance, and filings costs
- Conflict resolution issues
- PPP may not be feasible for smaller projects or projects done for BPL families.
- Different types of PPP- existing projects
-
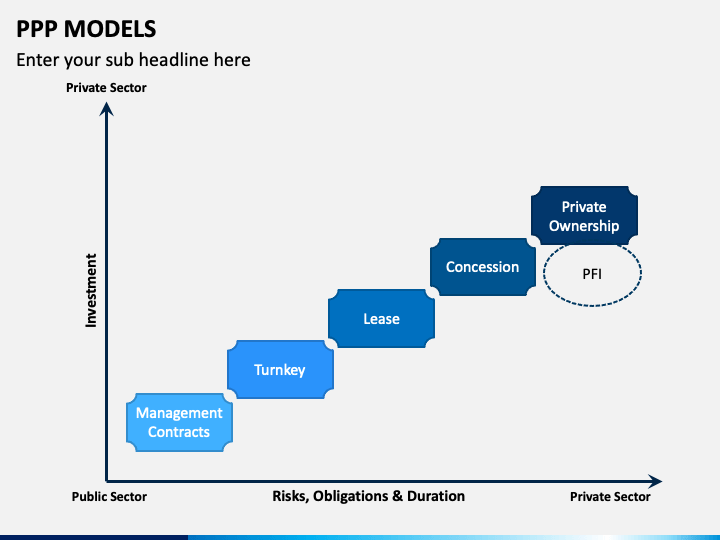
- 1) Management or service contract
- It's a contractual agreement for the management of part or whole public enterprise. For example- a specialized port terminal for container handling by the private sector.
- Management contract allows private sector skills to be brought into service service delivery however the public sector retains the ownership of the facility
- A private contractor is paid a fee to manage and operate and the payment is generally performance-based. Usually, the contract period is short-term (3 to 5 years).
-
Advantages-
- less risk due to a shorter duration
- Least no. of conflicts
Disadvantages-
- Almost all risk is taken up by the public sector,
- less incentive for the private player to invest
- 2) Turnkey management project
- It is the traditional public sector procurement model for infrastructure facilities. Generally, a private player is selected through a bidding process.
- Private player designs and builds facilities for a fixed fee which is one of the criteria for selecting the winning bid. The scale of investment by the private player is generally low and for a short-term period.
- 3) Affirmage/ Lease
- In this category of arrangement, the leaseholder is responsible for operating and maintaining the infrastructure facility that already exists.
- Generally, the operator does not require to make any large investments except in the case where this model is implemented with another PPP model. Example- Build-lease-Transfer.
- The difference between Affirmage and a lease is technical. Under the lease, the operator retains the revenue collected from the customer and makes a specified lease payment to the contracting authority. Under an Affirmage, the operator and the contracting authority share the revenue.
- 4) Concessions
- In this form of PPP, government grants specific rights to a private player to build and operate a facility for a fixed period of time.
- In concessions, payments can take place both ways i.e. the private sector pays for concession rights and the government pays the private player for providing certain services. Usually, such payment by the government may be necessary for making projects commercially viable.
- Area concessions- The private player is responsible for the full delivery of services in a specified area including operation, maintenance, construction, and rehabilitation of the systems. In these projects, the private player designs builds, operates, and finances the project, although the ownership is still retained by the government during the concession period.
The Topic for the next class:- Hybrid Annuity model, EPC, and BOT models.